 Does a brand new human need an injection of Hepatitis B vaccine?
Does a brand new human need an injection of Hepatitis B vaccine?
The Hepatitis B vaccine is a good vaccine for new parents to start researching, because the CDC, most hospitals, and doctors will recommend that your baby receive this shot in the first day or days after birth. It is critically important for parents to understand the facts about both the disease and the vaccine.
This 10 minute video by the ThinkTwice Global Vaccine Institute is based on information from the Vaccine Safety Manual by Neil Z. Miler. Important issues are clearly outlined with references to published scientific data.
The highest risk groups for Hepatitis B viral infection are heterosexuals engaging in sex with multiple partners, prostitutes, active homosexuals, and IV drug users.
Infants and children are at very low risk for Hepatitis B infection. Less than 1% of all cases of Hepatitis B in the U.S. are among children under 15 years. If the intent for the vaccine was to provide life-long protection to those who may develop Hepatitis B later in life, research shows that among those who mount an initial response to Hepatitis B vaccination, up to 50% have no evidence of immunity as soon as five years after completing the three-shot series. For infants vaccinated at birth, any benefit is gone well before they would become sexually active or use IV drugs.
There are two different single Hepatitis B vaccines available. Hepatitis B is also commonly added by manufacturers in combination vaccines, such as Pediarix (A combination vaccine for diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, hepatitis B, and polio.) Notice an excerpt of the Pediarix ingredients: “Each 0.5-mL dose contains aluminum salts as adjuvant (not more than 0.85 mg aluminum by 14 assay) and 4.5 mg of sodium chloride. Each dose also contains ≤100 mcg of residual formaldehyde and ≤100 mcg of polysorbate 80 (Tween 80).”)
-
Engerix-B
“Each 0.5-mL pediatric/adolescent dose contains 10 mcg of HBsAg adsorbed on 0.25 mg aluminum as aluminum hydroxide.”
“ENGERIX-B contains the following excipients: Sodium chloride (9 mg/mL) and phosphate buffers (disodium phosphate dihydrate, 0.98 mg/mL; sodium dihydrogen phosphate dihydrate, 0.71 mg/mL).”
http://www.fda.gov/downloads/BiologicsBloodVaccines/Vaccines/ApprovedProducts/UCM224503.pdf page 10 – 11
An important point to note is that the Hep B vaccine was followed for 5 days in safety trials.
“Dr. Stanley Plotkin, widely considered the world’s leading authority on vaccines, is questioned [under oath] by ICAN Lead Attorney Aaron Siri, Esq. about the pre-licensure safety testing of the Hepatitis B vaccine, a vaccine given to babies in their first days of life in the U.S. FDA Documents reveal the vaccine was followed for safety for just five days in the trials.” https://thehighwire.com/ark-videos/hepatitis-b-vaccine-safety-tested-for-just-five-days/
-
Recombivax HB
Is produced from cultures of yeast. Soy, formaldehyde, and aluminum are among the ingredients used in the formulation. Each .5 ml of the vaccine contains .25 mcg. Babies are given .5mL dose which would contain .25 mcg of aluminum. It is recommended to give 3 doses at 0, 1 and 6 months. (VPI, Page 1) After receiving all three doses, babies would have received .75 mcg of aluminum. There have been no scientific studies on the impact of aluminum on an infant. One study showed that the aluminum was not immediately found in either blood or urine. The conclusion was not explored: where is the aluminum? Since the aluminum was not excreted, it must be in the organs, bones or brain.
Neither version of the Hepatitis B vaccine has been evaluated for its carcinogenic (does it cause cancer?) or mutagenic potential (does it impact the genetic potential?), or its potential to impair fertility. You can read this in the vaccine package insert under section 13.1. Follow the link or see the copied information at the end of this blog. https://www.fda.gov/media/119403/download?attachment
Have there been any adverse reactions to the Hepatitis B vaccine?
Engerix Post Marketing Experience (page 8)
“This list includes serious adverse events or events that have a suspected causal connection to components of ENGERIX-B. Because these events are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to the vaccine.
Infections and Infestations: Herpes zoster, meningitis.
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: Thrombocytopenia.
Immune System Disorders: Allergic reaction, anaphylactoid reaction, anaphylaxis. An apparent hypersensitivity syndrome (serum sickness-like) of delayed onset has been reported days to weeks after vaccination, including: arthralgia/arthritis (usually transient), fever, and dermatologic reactions such as urticaria, erythema multiforme, ecchymoses, and erythema nodosum.
Nervous System Disorders: Encephalitis, encephalopathy, migraine, multiple sclerosis, neuritis, neuropathy including hypesthesia, paresthesia, Guillain-Barré syndrome and Bell’s palsy, optic neuritis, paralysis, paresis, seizures, syncope, transverse myelitis.”
The incidence of diabetes rose 60% in New Zealand following a massive Hepatitis B vaccine campaign.
VAERS (Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System) has (as of May 2016) 36,788 officially reported adverse reactions to the Hepatitis B vaccine. 14,800 were serious resulting in hospital stays, or life threatening. 781 people died.
Is the Hepatitis B vaccine effective? 3 doses are required. The duration of the protective effect is unknown. NEJM showed that antibody declined sharply or no longer existed in 42% of recipients after 5 years.
When the Hepatitis B vaccine was first introduced for infants in 1994, 87% of pediatricians and family practice physicians did not believe it was needed by their newborn patients.
Why is the Hepatitis B vaccine given to newborns?
Early Hepatitis B vaccination strategy was targeting and limited to high risk individuals. The vaccine was not well received by this target population group. Since authorities were not able to get high risk groups to accept the vaccine, they decided to target babies who were easily accessible via baby wellness appointments.
Since babies are unlikely to contract Hepatitis B and vaccine efficacy declines after a few years, babies are currently being exposed to all the risks of this injection for zero expected benefit
Vaccine exemptions are available. In 47 states you are allowed a religious and/or philosophical exemption. You can submit your letter of exemption in lieu of proof of vaccination for school entrance.
In California, Mississippi, and West Virginia you must have a medical exemption in order for your child to attend school without this vaccine. However, if you live in those states, my personal recommendation would be to delay the vaccines as long as possible while praying and working with others to change the legislation to allow freedom of choice. Where there is risk, and there is great risk with the Hepatitis B vaccine, there MUST be a choice.
Babies are precious. As parents, we are entrusted with their care. All vaccine manufacturers carry no liability if our child suffers any vaccine damage. We need to make sure we base our decision on facts.
Author: Becky Hastings, wife, mother, grandmother, breastfeeding counselor with a passion for helping parents raise healthy babies. Navigating information can be confusing. We need to find the truth.
Below you will find brief excerpts from the vaccine package insert for one of the Hepatitis B vaccines. All vaccine package inserts are available on the FDA website. See link below.
11 DESCRIPTION
“RECOMBIVAX HB Hepatitis B Vaccine (Recombinant) is a sterile suspension of non-infectious subunit viral vaccine derived from HBsAg produced in yeast cells. A portion of the hepatitis B virus gene, coding for HBsAg, is cloned into yeast, and the vaccine for hepatitis B is produced from cultures of this recombinant yeast strain according to methods developed in the Merck Research Laboratories.”
“The antigen is harvested and purified from fermentation cultures of a recombinant strain of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae containing the gene for the adw subtype of HBsAg. The fermentation process involves growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae on a complex fermentation medium which consists of an extract of yeast, soy peptone, dextrose, amino acids and mineral salts. The HBsAg protein is released from the yeast cells by cell disruption and purified by a series of physical and chemical methods. The purified protein is treated in phosphate buffer with formaldehyde and then coprecipitated with alum (potassium aluminum sulfate) to form bulk vaccine adjuvanted with amorphous aluminum hydroxyphosphate sulfate. Each dose contains less than 1% yeast protein. The vaccine produced by the Merck method has been shown to be comparable to the plasma-derived vaccine in terms of animal potency (mouse, monkey, and chimpanzee) and protective efficacy (chimpanzee and human).”
“The vaccine against hepatitis B, prepared from recombinant yeast cultures, is free of association with human blood or blood products.”
“All formulations contain approximately 0.5 mcg of aluminum (provided as amorphous aluminum hydroxyphosphate sulfate, previously referred to as aluminum hydroxide) per mL of vaccine. In each formulation, hepatitis B surface antigen is adsorbed onto approximately 0.5 mg of aluminum (provided as amorphous aluminum hydroxyphosphate sulfate) per mL of vaccine. The vaccine contains <15 mcg/mL residual formaldehyde. The vaccine is of the adw subtype. (Page 6-7)”
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
RECOMBIVAX HB has not been evaluated for its carcinogenic or mutagenic potential, or its potential to impair fertility. (Page 7)
http://www.fda.gov/downloads/BiologicsBloodVaccines/Vaccines/ApprovedProducts/UCM110114.pdf
For further reading on Hepatitis B vaccine, The Insanity of the Hepatitis B Vaccination, by Michelle Goldstein is a mental health therapist who is passionate about holistic health, natural healing, nutrient-dense foods and the politics that impact them.








 I thought I was being a good parent. When I questioned vaccines at the doctor’s office, the doctor and nurses pushed them, saying it was for my children’s safety. I concluded that I was just being paranoid. I did think, when I signed that waiver regarding vaccine liability, it was weird. I thought ‘Why do I need to sign this? It doesn’t make sense…’
I thought I was being a good parent. When I questioned vaccines at the doctor’s office, the doctor and nurses pushed them, saying it was for my children’s safety. I concluded that I was just being paranoid. I did think, when I signed that waiver regarding vaccine liability, it was weird. I thought ‘Why do I need to sign this? It doesn’t make sense…’



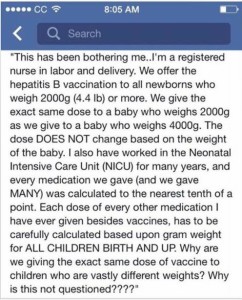 A registered nurse who works in labor and delivery explained to me that the hepatitis B vaccination is given, after the consent of the parent, to all newborns weighing 2000g (4.4lb) or more.
A registered nurse who works in labor and delivery explained to me that the hepatitis B vaccination is given, after the consent of the parent, to all newborns weighing 2000g (4.4lb) or more.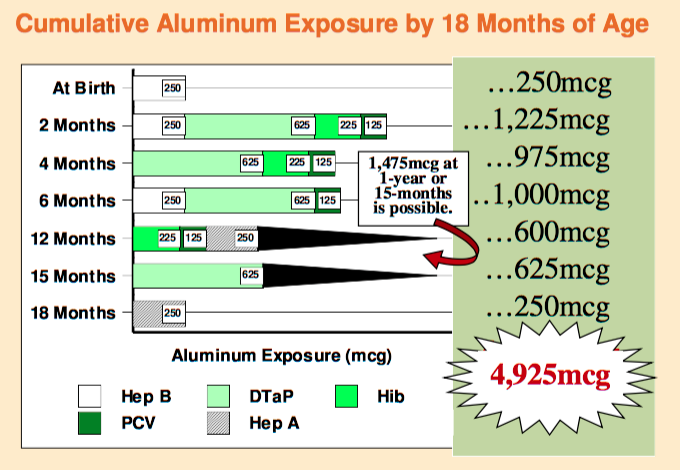






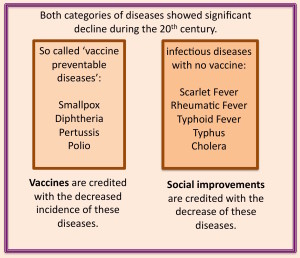 For over half a century medical and nursing students have been trained that vaccines were the reason children and adults stopped dying from diseases for which there are vaccines. They are taught that there are two categories of historical diseases: ‘vaccinatable’ and ‘non-vaccinatable’. Both categories of disease diminished in incidence and mortality (causing death) over time, but the reasons given for this decrease depends solely on whether there was a vaccine that managed to reach the market, or not.
For over half a century medical and nursing students have been trained that vaccines were the reason children and adults stopped dying from diseases for which there are vaccines. They are taught that there are two categories of historical diseases: ‘vaccinatable’ and ‘non-vaccinatable’. Both categories of disease diminished in incidence and mortality (causing death) over time, but the reasons given for this decrease depends solely on whether there was a vaccine that managed to reach the market, or not.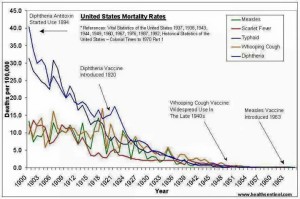


 Author Becky Hastings: I’m just a wife, mom, grandmother, passionate follower of Jesus, fitness trainer, health promoter, breastfeeding counsellor helping moms for 22+ years, and someone who seeks to research, understand and share truth so people can make wise choices in our crazy mixed up, deceived world!
Author Becky Hastings: I’m just a wife, mom, grandmother, passionate follower of Jesus, fitness trainer, health promoter, breastfeeding counsellor helping moms for 22+ years, and someone who seeks to research, understand and share truth so people can make wise choices in our crazy mixed up, deceived world!